1. Manual Actions & Penalties By Google
You may have been breaking Google’s guidelines or posting spammy and harmful content without realizing it.
These things can incur a well-deserved manual action.
How To Uncover Manual Actions & Penalties
To find out if you have been smacked with a penalty, look inside Google Search Console.
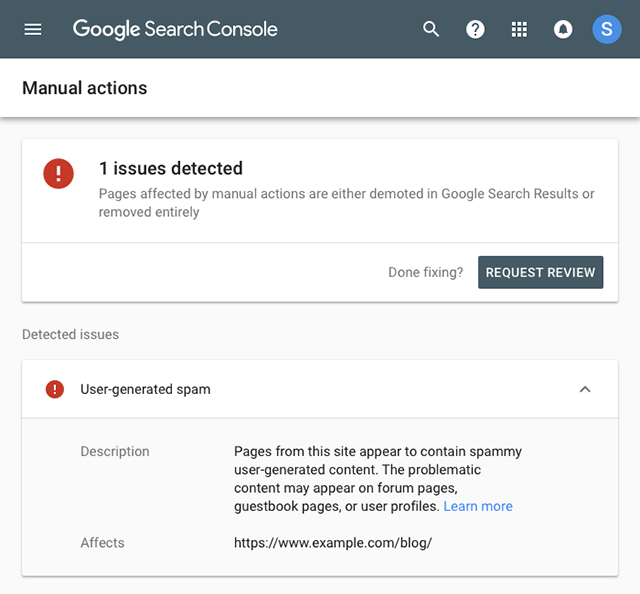 Screenshot from Google Search Console, January 2024
Screenshot from Google Search Console, January 2024If it says anything other than “No issues detected,” you are in trouble.
Luckily, Google will describe what they did and why, so you will know right away how to lift the sanctions against your site. Sometimes it will be as easy as deleting offending content.
2. Inefficient Internal Linking
Hyperlinks do much more than just let users jump between pages.
They have two important jobs:
- Transfer authority from one page to another.
- Shape the user journey.
These jobs apply both to external and internal links. While the content of an externally linked page is often out of your control, the internal links are fully under your control, so you can’t afford to neglect how you use them.
Otherwise you will end up with a site that neither ranks in Google nor is user-friendly.
How To Make Your Links User-Friendly & Google-Friendly
To interlink the pages on your site efficiently:
- Make your links’ anchor texts descriptive. Users must be able to look at a link and immediately understand where it leads.
- Link from pages with high authority to pages with lower authority. That way, low-authority pages can receive more authority and rank higher. Find pages that could benefit from it with WebCEO’s Internal Links tool.
- Use a navigation bar and a footer. They contain links to some of the most important pages (like homepage, FAQ, About Us, Contact Us) which users must be able to find at any time.
- Create topic clusters. A good practice for increasing your site’s authority is creating multiple pages on several related topics and linking them together.
- Make the user journey as short as possible. An unwritten three-click rule states that users must be able to find anything they want in three clicks or fewer. Even if no evidence supports this rule’s impact on SEO, it’s hard to deny that it’s good for user experience.
3. Lack Of User Accessibility
As we know, not all users are perfectly healthy. Old age, diseases, or disabilities can make it very hard or even impossible to comfortably browse the Internet.
If your website does not cater to all levels of users, it becomes less user-friendly, which gets in the way of a positive user experience.
It’s so important that it’s even required by law. You can’t fix a lawsuit with SEO, so don’t tempt fate.
You want your site to be available to as many people as possible – and for that purpose, there is user accessibility.
How To Improve The User Accessibility Of Your Website
Is your site accessible? There are many tools to find that out, like ARIA by EquallyAI.
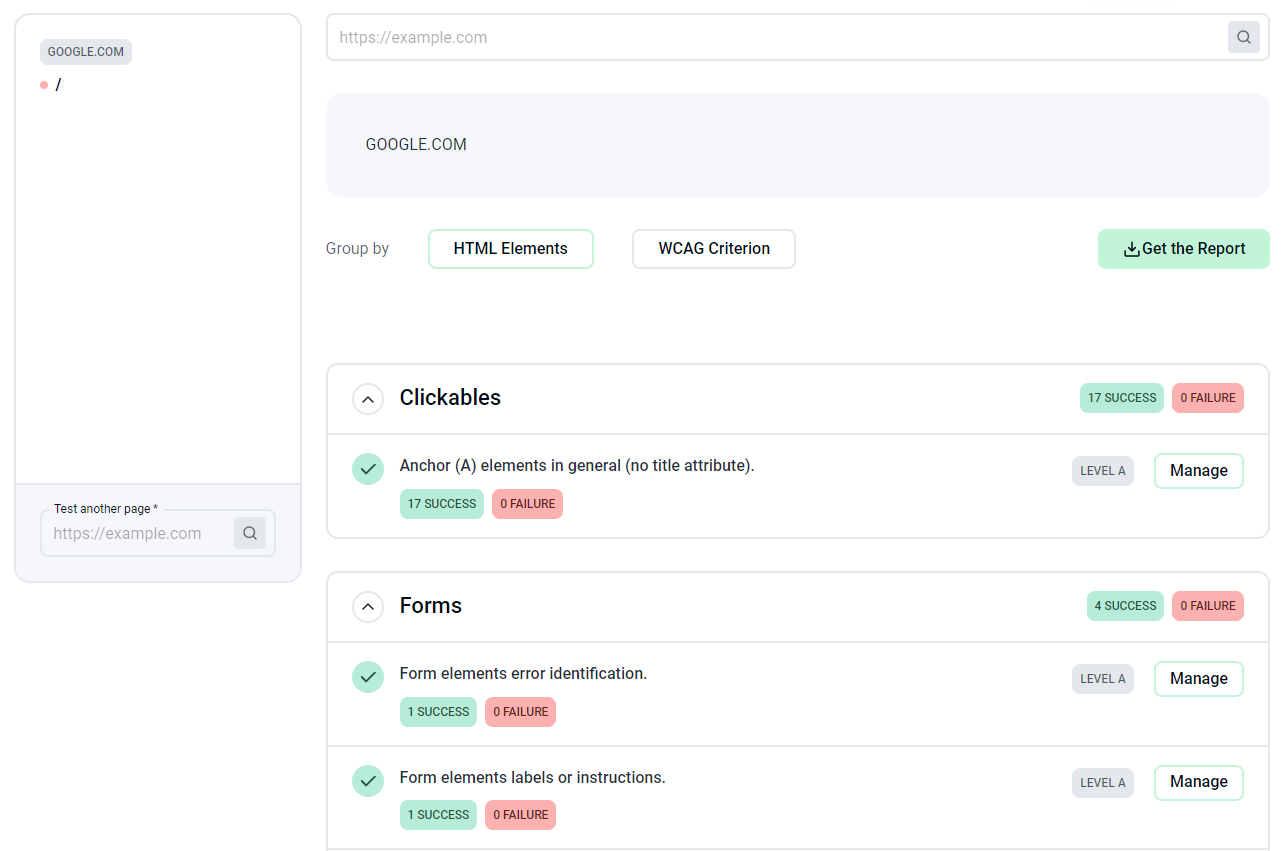 Screenshot from EquallyAI, January 2024
Screenshot from EquallyAI, January 2024World Wide Web Consortium provides several extensive resources for designing and developing accessible websites.
If your site doesn’t pass the accessibility test, or if user feedback lets you know about any problems, you should apply practices from those resources.
4. Using The HREFLANG Tag Incorrectly
If you target a multilingual audience (for example, with an ecommerce site), you need to watch out for this one.
You don’t want to ruin the users’ experience with a language barrier.
The hreflang tag’s job is to show the visitors the version of your site they can read, based on their location and language.
How To Use The HREFLANG Tag Correctly
A properly coded HREFLANG tag should look similar to:
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/en" hreflang="en-GB" />Parts Of An HREFLANG Tag
The “en-GB” attribute means it targets English-speaking users in the United Kingdom. “En” is the language code (ISO 639 format) and “GB” is the region code (ISO-3166-1 alpha-2 format). Always remember to refer to these Wikipedia links to pick the correct codes!
If the tag has the wrong attribute or none at all, you risk giving your visitors a bunch of text they can’t read or navigate, making your site useless to them. Kiss those conversions and rankings goodbye, say hello to bounce rates.
So make sure your hreflang tags are in order by scanning your site with WebCEO’s On-Site Issues Overview tool.
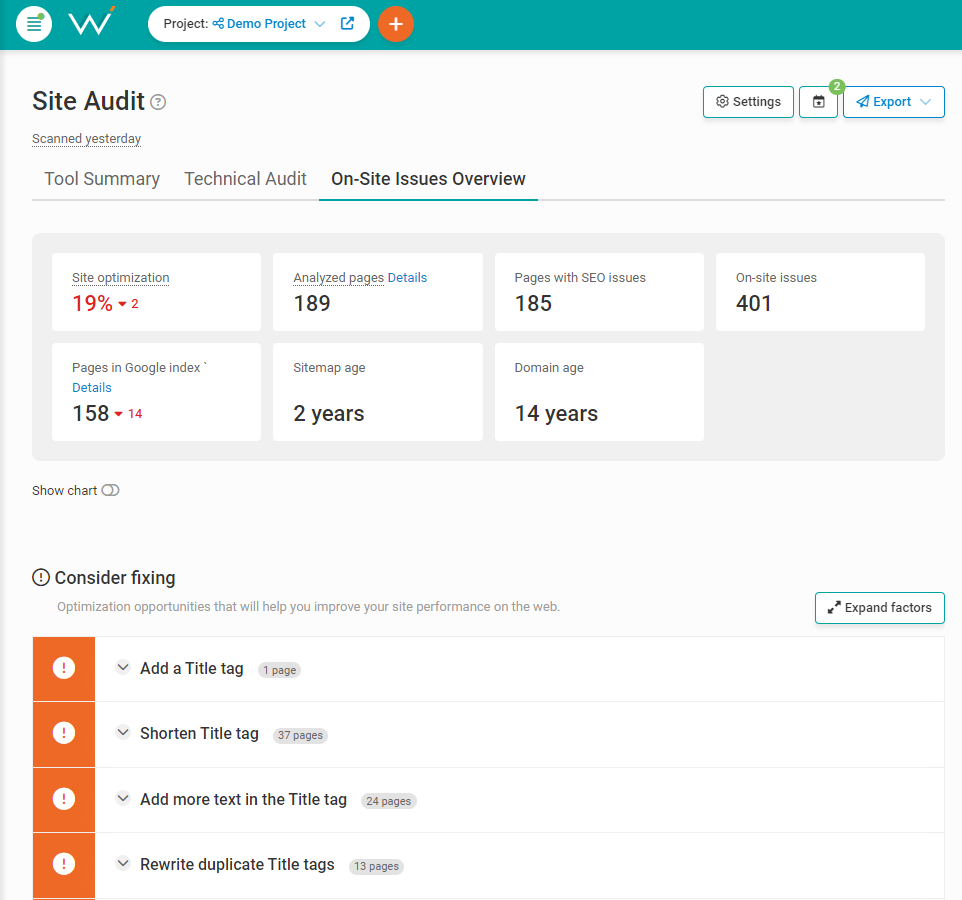 Screenshot from WebCEO, January 2024
Screenshot from WebCEO, January 2024Although, the hreflang tag isn’t a perfect solution. There’s always a non-zero chance the user’s native language isn’t even used wherever they reside. For these cases, and for all others too, it’s best to have an option to manually switch between the languages on your site.
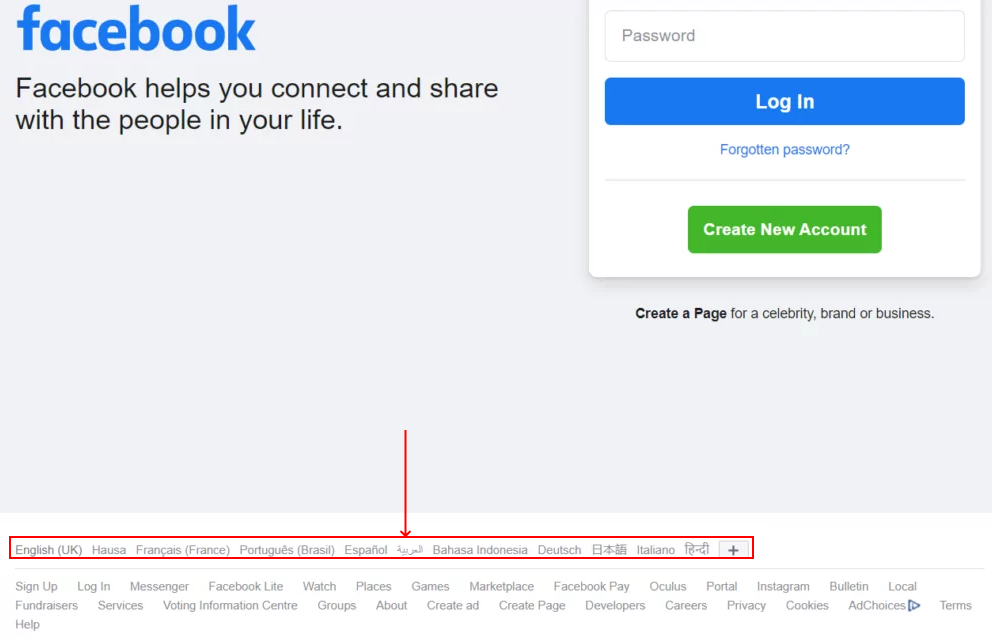 Screenshot from Facebook.com, January 2024
Screenshot from Facebook.com, January 20245. Opening New Links On The Same Page
This problem can affect your rankings by diverting traffic before a conversion.
While Google have an opinion about the links’ target=”_blank” attribute, it’s still a good idea to use it on your links.
Why Should You Open All Links In A New Tab?
When the link opens in the same tab, users leave the page they were on – often before there was a conversion. That makes your high-ranking pages less useful. And if it keeps happening, Google will agree and lower the rankings.
Fortunately, the solution is simple: include the target=”_blank” attribute in your links’ HTML code. Some platforms, like WordPress, often add this attribute automatically.
Important! The target=”_blank” attribute should always be used together with rel=”noopener” or rel=”noreferrer” for security reasons. If you inadvertently link to a shady page, either of these attributes will prevent it from gaining access to the tab from which the user opened the link, protecting both your site and the user’s device.
In other words, the HTML code for a secure link will look like this:
<a href="https://example.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Your link</a>6. Poorly-Optimized Images
Image quality is a very obvious factor, so let’s assume your site uses only good-looking images. But at the same time, this factor is a double-edged sword: with high quality comes high file size.
And large images affect your site loading speed.
Website Image Best Practices
You should never sacrifice the quality of your visuals. So what can you do instead?
- Save your images in the most optimal format. The logo icon should be ICO or SVG, large photos should be JPG, and you can use WEBP instead of GIF (although not all browsers support WEBP).
- Manually set height and width. Shave off all the excessive pixels.
- Merge images if they are placed right next to each other.
- Compress your images with software like TinyPNG.
And then upload them.
7. Website Caching Issues
In addition to poorly optimized images or assets like CSS and Javascript files, your site could be loading slowly because of caching issues.
A cache is where browsers store a website’s elements upon visit.
For example, a website’s logo is the same on every page, so once it’s stored, your browser doesn’t need to load it anew – instead, it will just retrieve it from cache, and your site will load faster.
How To Properly Cache A Website
If your website suddenly starts showing resistance to caching, you should check the .htaccess file on your server.
The .htaccess file can be used for many cool things, like password-protecting your site or customizing your error 404 page.
It can also be used to set expiration dates for the cached resources.
Open your file and look for code like this:
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive on
ExpiresDefault "access plus 2 days"
ExpiresByType image/jpg "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/gif "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/css "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/javascript "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/ico "access plus 1 year"
ExpiresByType text/html "access plus 600 seconds"
</IfModule>If there’s nothing like that at all, feel free to copy and paste this example.
Otherwise, tweak those “access plus time” bits to your preference or add entries for additional file types.
The trick is to set a long expiration period for elements that don’t change often, like the logo icon. That way, they will stay cached for as long as you decide.
8. Failing To Match User Search Intent
You’ve probably used SEO tools to find the best keywords: long-tailed, with a high search volume, not too competitive.
You’ve put them in all the right places: title, description, URL, headings, and throughout the text too.
Yet your site rankings and visits aren’t increasing. Why not?
It’s possible you forgot to account for the most important factor in keyword optimization: user search intent.
What Is User Intent In SEO?
You don’t want to bring users without purpose.
You want them to do specific things: learn, discuss, subscribe, purchase, share, and so on.
This variety makes it possible to categorize user search intent under several types:
- Informational (learning new information).
- Navigational (looking for a specific website).
- Commercial (looking for a product).
- Transactional (buying a product).
- Locational (looking for a place or information about a place).
- Seasonal (tied to a time period or a date, like Christmas).
That’s why not only your content, but your keywords must reflect it as well. And with so many types, it’s easy to make a mistake and choose the wrong keywords for the job. Knowing the difference between them can make or break your SEO.
How Do I Implement User Intent Into My SEO Strategy?
Target users with even higher accuracy by remembering the stages of the keyword funnel:
- Awareness: the user has a need and starts searching for a solution, possibly not knowing yet what it could be. Example: buy laptop.
- Interest: the user narrows down and explores the options. Example: best gaming laptops.
- Action: the user knows exactly what they want and intends to get it. Example: laptop Lenovo IdeaPad Gaming 3.
Choose the best keywords that reflect these stages and you’re good to go.
9. Accumulation Of Harmful Backlinks
Backlinks are necessary for building up your site’s authority – and site rankings. It’s a crucial step in SEO: very hard to do right and incredibly easy to mess up.
Having no backlinks at all is bad, but it’s even worse to have lots of low-quality backlinks.
If you don’t check your link profile from time to time, you won’t even know you have this problem and need to fix it.
How To Find Harmful Backlinks & Remove Them
First, scan your backlinks with WebCEO’s Toxic Pages tool.
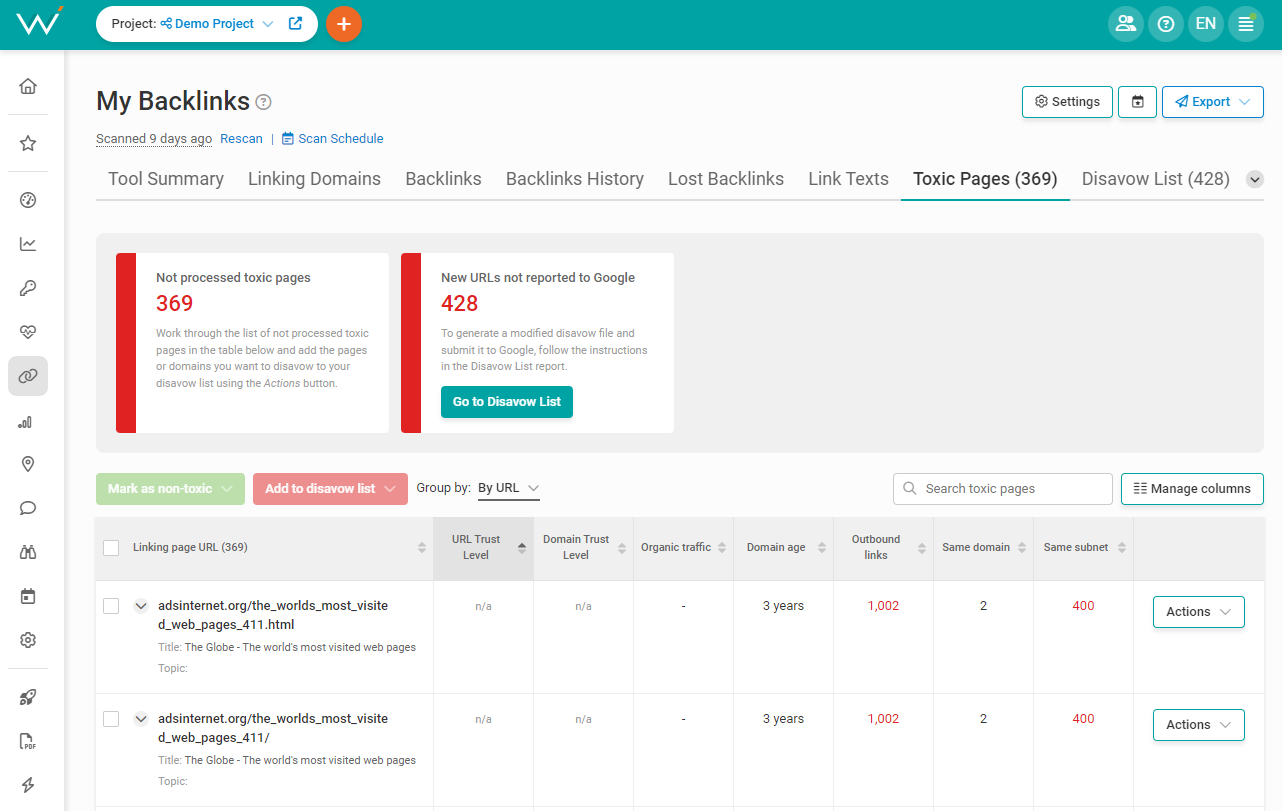 Screenshot from WebCEO, January 2024
Screenshot from WebCEO, January 2024It will look through all of your site’s backlinks and display the potentially harmful ones in a table. If you find any backlinks from sites you actually trust, you can keep them. But the ones that do look bad have to go.
Your options are:
- Delete those backlinks yourself.
- Ask somebody who can edit the linking site to delete them.
- Use Google Disavow (in-built in the Toxic Pages tool) to make Google ignore those links.
10. Failing To Follow SEO Trends
Search engine optimization has come a long way since its inception.
Many new things were introduced, many old things stopped working, and even more were improved upon and made more accurate. And this process continues.
So if you don’t monitor the SEO news and innovations, you may find that your SEO efforts aren’t effective anymore.
Make it a habit to read SEO news regularly (like on this very site). Pay attention to any important updates – especially to Google’s core algorithm updates. When those roll out, SEO changes drastically for everybody.
The more you know about different SEO problems, the easier you can identify and fix them in time. All you need is a good eye and reliable tools. Stay sharp and check your site for signs of trouble often.

