Is it testworthy, or is it untestworthy?
There’s a fine line between optimizations and experiments. Testing something is an exercise in curiosity, whereas optimizing a thing is an act of certainty.
If we know the outcome of a given activity before we perform that activity, we’re in optimization territory. For example, if you’ve discovered a load of orphaned pages, then the act of internally linking to those pages is highly likely to result in a positive outcome. We can deem this scenario, “untestworthy” (yes, I know that’s actually a word).
But, as we’ll discuss here, SEO includes a vast array of activities where the outcomes of our work are either uncertain or difficult to predict. Think about the last time you experienced a site migration. Were you certain that the new site would perform better than the original? This might be a scenario that we’ll deem, “testworthy.”
In short, a testworthy activity is one where we don’t know the ending until we measure our outcomes with data.
Measuring our SEO tests
The step-by-step measurement processes and techniques for conducting SEO experiments fall outside the scope of this article, so if you’re reading this and asking yourself, “how exactly do I run an SEO experiment from start to finish?”, here are a couple links to resources that can assist you in learning the nitty-gritty specifics of setting up and measuring SEO experiments:
For each of the experiments below, I will assume a time-based measurement technique. Although some of the ideas here can be tested using an A/B split testing technique, not all of them can.
Curious about time-based techniques? I cover them in detail in this guide.
A word on statistical significance
One final note to remember. Statistical significance, i.e. when your results can be confidently attributed to your testing criteria, is a sexy concept, but one sobering reality of SEO testing is that statistical significance can only be achieved through rigorously advanced split testing.
Time-based SEO experiments provide us with directional learnings, not absolute conclusions. Advantages of experimenting in this way include the ability to react more quickly, use up fewer resources, and the flexibility to experiment in nearly all search environments where split testing cannot.
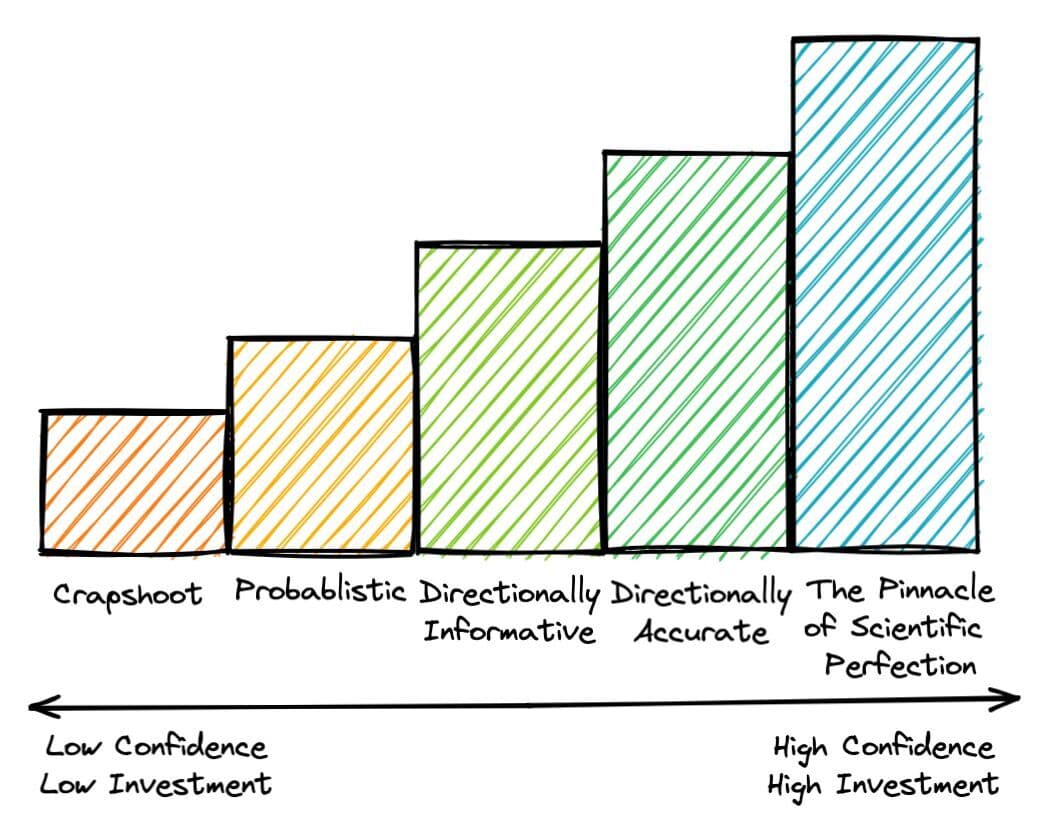
Here’s one way to visualize how non-significant tests remain valuable. On the left end of the spectrum, there are the crapshoot experiments: low confidence, low investment initiatives that provide less reliable insights. Further to the right, we can begin categorizing experiments according to higher confidence intervals and higher resource investments. Somewhere in the middle, there are a great many SEO tests that provide directional insights, even when our directional insights aren’t guaranteed with the promise of scientific certainty.

With this in mind, I’ve put together a list of five inconspicuous SEO tests that appear “untestworthy,” but are actually SEO tests disguised as optimizations.
Test in disguise #1: URL switching

A URL switch test is really very similar to SEO title testing. The idea behind URL switch tests is simple: like page titles, we know that URLs are heavily weighted ranking factors, so if we find that there are URLs that look under-optimized or misaligned with our target terms and search intents, then we can build a hypotheses for testing a new URL and redirecting the original URL.
Some of you might be silently blowing a fuse right about now, and for good reason. URL switch tests can be very risky. If your original URL has already generated a substantial number of links (internal or external) I would exercise extreme caution before running a URL switch test.
As you probably know by now, redirects have the potential to backfire, and if your test fails, cannot be rolled back to the original URL variant as easily as a title test can be rolled back.
But this shouldn’t scare you if you are running a URL switch test in lower-risk scenarios. I have seen many successful URL switch tests in scenarios where the target URL was either freshly-launched, had too few links pointing to it, or where the URL was so ineffective that an experiment was justifiably worth the risk.
How to run a URL switch test
Check the URL’s current traffic levels. Higher traffic levels = higher risk.
Check the URL’s internal and external links. Internal links can be updated, but external links can still lose strength as you pass them through a 302/301.
- If the risk is within your level of tolerability, clarify what your new hypothesis and URL test variation will be.
Example hypothesis: Changing the URL string from a partial match string to an exact match string will align our page more closely with the target keyword and increase rankings and clicks for the target keyword.
Change the URL from the control URL to the variation URL.
Add a 302 temporary redirect from the control to the variation, submit the URL for re-indexation in Google Search Console (GSC), and benchmark the date that this is completed on.
- Wait 2-6 weeks to measure the clicks before vs. clicks after for equal time durations and days of the week in GSC.
For example: If your measurement period (after data) begins on a Thursday and ends on a Sunday, then I recommend comparing with an equivalent time duration in GSC that also begins on a Tuesday and ends on a Sunday just prior to the experiment launch date (before data). For most websites, the click patterns on weekends will be lower than on weekdays. Using the same days of the week and time durations allows you to control for these differences in daily click patterns.
The optimal time-range is situation-dependent. Pages that generate high click volumes can be measured closer to the two-week time-frame, while pages that generate lower click-volumes will need to run longer.
Caution: If the risk to this page is high, you may want to check in periodically during the first few days to make sure that performance doesn’t drop unexpectedly.
- When measuring performance, use the “compare URLs” feature in GSC. This lets you check both the control URL and the variation URL simultaneously.
- After you’ve gathered enough data to make a directionally-sound judgment call about which URL performs better, do one of the following:
If the new variation performed better: Change the 302 temporary redirect to a 301 permanent redirect and update all internal links to reflect the new URL.
If the original control URL performed better: Remove the 302 redirect. [Optional: you may want to add a new redirect from the failed variation URL back to the original control URL to speed up the re-indexation process.]
Resubmit the final URL in Google Search Console and periodically monitor the performance after the test has ended to ensure that performance remains positive.
Test in disguise #2: Content refreshes

Isn’t a content refresh a given? We know that refreshing content is good for SEO, so why does it need testing?
Yes, content refreshes are incredibly important and this is an activity that has been proven successful time and time again. However, not every content refresh yields positive results.
Even though it isn’t the norm, content refresh projects can occasionally result in traffic losses, and perhaps equally frustrating, many refresh projects can turn out neutral results. This means that all of that precious time and energy that we spent rewriting and republishing a piece of content failed to produce the outcome that we intended.
For these reasons, it’s important to figure out if our investments in these projects have achieved their desired positive outcomes or not. That’s where SEO testing comes into play.
How to run a content refresh SEO test
Perform your content refresh project exactly as you otherwise would, according to your own content team’s workflow. Make sure to save all of the original files, in case you need to revert back to the original content.
On the date of republication, submit the page URL to Google Search Console to be re-indexed and benchmark the date.
- Wait 2-6 weeks to measure the clicks before vs. clicks after in GSC.
Once again, keep in mind that the best time duration will vary based on the click volumes that each page receives.
- After you’ve gathered enough data to make a directionally-sound judgment call about which URL performs better, do one of the following:
If the variation performed better: Congrats! Report the results to your team and keep the change.
If the control performed better: Reinstate the original content and files. Then, re-index the page and continue monitoring performance to look for rebounding traffic.
Test in disguise #3: Section rearrangement

A section rearrange test is just what it sounds like. The hypothesis for these experiments is that if we can reprioritize some of the on-page content, elements, or components, then we might be able to influence the page’s rankings and traffic coming in.
This can work particularly well, if the page section that addresses our audiences’ main search intents is either buried deep below the fold, or if it requires extra steps for the user to access that content.
For simplicity’s sake, let’s use the example keyword: “email ideas for cold outreach.”
This keyword appears to have a lot of demand from users who are looking for specific email templates and phrasings that they can use in their outreach campaigns.
Now, let’s assume that you’ve got a blog post on this exact topic, but the exact email templates and scripts that users are searching for are buried at the end of your posts, well past a dozen other sections of content that don’t satisfy their search demand. This might be a great case for running a section rearrange test.
The idea is, if you can reprioritize those pieces of information that users are looking for from the bottom of your page to the top of your page, Google is likely to notice the prioritized content as a better match for users to quickly access the information they want. Thus, rankings and traffic may improve in the same way they might improve with a content refresh project.
Added bonus: it’s faster than rewriting new content!
How to run a section rearrange SEO test
Look for pages that are underperforming, and that have addressed a users’ primary search intent somewhere deep within the page.
Rearrange the page sections in a way that might create a better experience or flow for the readers.
Launch the new page (but remember to save the original control page files), re-index in Google Search Console, and benchmark the date.
- Wait 2-6 weeks to measure the clicks before vs. clicks after in GSC.
Again, keep in mind that the best time duration will vary based on the click volumes that each page receives.
- After you’ve gathered enough data to make a directionally-sound judgment call about which URL performs better, do one of the following:
If the variation performed better: Congrats! Report the results to your team and keep the changes.
If the control performed better: Reinstate the original content and files. Then, re-index the page and continue monitoring performance to look for rebounding traffic.
Test in disguise #4: Content removal

This test is the SEO-equivalent of what CRO professionals call “a takeaway test.”
In digital marketing, there are times when less really is more, so the idea for this experiment is, if we just trim out certain items — whether those might be page elements, or less-helpful content sections — then the removal process could lend itself to creating a tighter, stronger webpage.
In a CRO-driven takeaway experiment, a CRO professional might notice certain elements that distract users or get in the way of a conversion path.
This concept works just a little bit differently for SEO if our goal is to improve rankings and traffic performance. For SEO, content removal experiments are just a matter of “trimming the fat” from our content and page elements.
When analyzing your top pages, ask yourself if you see any sections, paragraphs, or sentences which deviate from the information that the search audience really came for. You might be surprised to see how much of the content we create is actually worthless for our users.
How to run a content removal SEO test
Scan for high-value pages and posts that may be hitting a wall with rankings and traffic performance.
Make sure to analyze the top keywords and SERPs so that you can get very clear on which primary and secondary search intents the users predominantly wish to see and read about.
Scan your page’s content with a dose of radical honesty to look for content that diverges from the information that you might want to see if you were a reader.
If your investigation turns up content and/or elements that don’t help the users, remove them and make sure to save the original control page files, just in case the experiment results are negative.
Launch the new page, re-index in Google Search Console, and benchmark the date.
- Wait 2-6 weeks to measure the clicks before vs clicks after in GSC.
Again, keep in mind that the best time duration will vary based on the click volumes that each page receives.
- After you’ve gathered enough data to make a directionally-sound judgment call about which URL performs better, do one of the following:
If the variation performed better: Congrats! Report the results to your team and keep the changes.
If the control performed better: Reinstate the original content and files. Then, re-index the page and continue monitoring performance to look for rebounding traffic.
Test in disguise #5: Featured snippets
This activity is one of my all-time favorites.
Treating our featured snippet answers like an SEO test is one of the ways that my teams have been able to accrue competitively high volumes of traffic and clicks in recent years.
When our team began to treat our featured snippets as experiments, rather than optimizations, we were able to learn much more about how to write better answers, and we were able to create processes for scaling up to higher quantities of featured snippet experiments. This meant more “at bats” for acquiring the answer box rankings, which meant faster traffic growth.
Much has already been covered about how to optimize for featured snippets. I’ll simply add a process for testing your featured snippet copy.
What’s more, featured snippet tests are one of the rare instances where statistical significance is undeniably attainable because the success measurement is binary. Either your experiment resulted in acquiring the featured snippet, or it did not. (Caveat: Some longer tail featured snippets may also be impacted by your experiments, but the impacts are generally negligible if you are targeting a strong primary keyword.)
How to run featured snippet tests
Identify opportunities where featured snippets are appearing in the SERPs, and where one of your pages ranks within the top 5 positions but is not occupying the answer box. (Tip: some of the current rank tracking solutions such as STAT make featured snippet identification much easier.)
Sort and prioritize featured snippet opportunities according to the opportunities that represent the highest value to your website. I recommend considering the traffic’s audience and conversion potential alongside the potential search volume.
Rewrite the portion of your article where the featured snippet is being targeted. This step is another one where the full context of featured snippet practices span outside the scope of this article, so you may want to check out resources like this if you’re not already familiar with featured snippet rewriting.
Periodically check in on your target answer box(s) and traffic over the next several weeks.
If at first you don’t succeed, test again! The great part about answer box testing is that you rarely need to revert to your control, and you can keep swinging until you hit the home run. In some cases, we’ve had to make as many as ten or more rewrite attempts before successfully capturing the featured snippet.
Repeat this process to run more experiments the remaining featured snippet opportunities that were identified in step one.
More SEO tests in disguise
This list is far from exhaustive.
As I alluded to earlier in the piece, I think that just about anything which requires measurement is a form of testing to some degree, regardless of whether or not this activity can be measured to true statistical significance.
If your team is investing any serious resources into activities like core web vitals, internal linking, E-A-T enhancements, site migrations, Schema markup, or UX changes, it’s usually wise to do a retrospective before and after analysis on whether or not that investment yielded a positive payoff.
Stacking up those experiments to figure out where your bets are paying off, versus where they are not paying off will start to steer your strategy and SEO knowledge toward more profitable outcomes.